Screen and test for systemic mastocytosis (SM) at the first signs of the disease1
A thorough workup should be initiated once SM is suspected based on hallmark symptoms (skin lesions, anaphylaxis, diarrhea) or other symptoms of mast cell activation1,3,4
Did you know?
Screening tools can help lead to an SM diagnosis.4
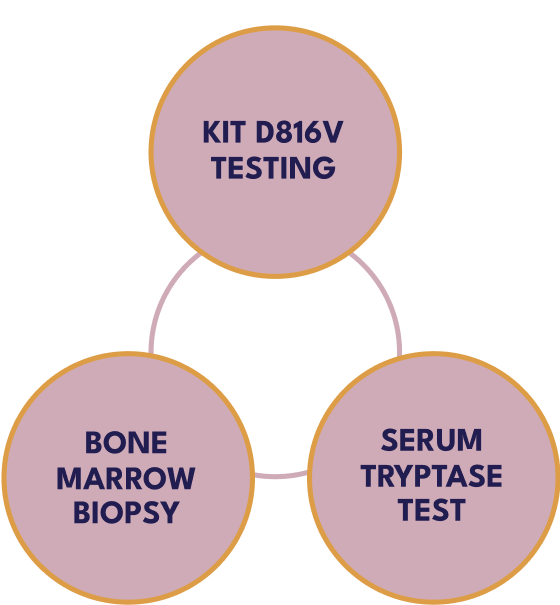
Testing serum tryptase levels and KIT D816V mutation in peripheral blood are 2 components to screen for SM.4
A bone marrow biopsy may be required for diagnosis.4
KIT D816V testing, used in peripheral blood, can be a first step to evaluate SM
The KIT D816V mutation is the main driver of disease in ~95% of SM cases.5-8
Low-sensitivity assays may fail to detect the KIT D816V mutation and potentially prolong diagnosis.9,10 It is recommended to use a high-sensitivity test for detection of KIT D816V.9,10 Quantitative digital PCR testing is commercially available with limits of detection ≤0.03%.9,10
Find a lab offering high-sensitivity KIT D816V assaysDetection of a KIT D816V mutation is a minor criterion for SM diagnosis.4 Further workup may be required to assess if a patient meets the diagnostic criteria for SM diagnosis.4
See SM diagnostic criteriaResources for hematopathologists
A guide to the integral role a hematopathologist
plays in the accurate diagnosis of SM
the hematopathologist
brochure
A tool to record patients’ diagnostic lab results in the assessment of an SM diagnosis
Download THE sm diagnosticcriteria reference sheet
A diagnosis of SM can be made using criteria established by the World Health Organization (WHO) and/or the International Consensus Classification (ICC)4,9*
Major criterion
Multifocal dense infiltrates of tryptase and/or CD117-positive mast cells†‡
Minor criteria
- >25% of mast cells are spindle-shaped or have an atypical or immature morphology‡
- KIT D816V mutation or other activating KIT mutation‡
- Elevated serum tryptase level, >20 ng/mL§
- Mast cells‡ express CD25, CD2, and/or CD30
It is important to explore the minor diagnostic criteria, as it is possible that up to
~43%
of SM cases
may not fulfill the major criteria.4,8
- *This highlights the combined key criteria based on the ICC and proposed changes to the WHO 5th edition guidelines and is not intended as diagnostic advice. Full guidelines are available from the WHO and ICC.
- †≥15 mast cells in aggregates.
- ‡In bone marrow biopsies and/or in sections of other extracutaneous organ(s).
- §This parameter is not valid in the presence of a myeloid AHN and may need to be adjusted in the case of known HɑT.
- AHN=associated hematological neoplasm; CD=cluster of differentiation; HαT=hereditary alpha-tryptasemia; KIT=KIT proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; PCR=polymerase chain reaction.
SM Provider Peer Directory
An online resource that lists the contact information of healthcare providers who have attested that they have experience managing patients living with SM and have volunteered to independently connect with peers who have questions about their medical experience.
See how patients with SM might present in your practice
EXPLORE HYPOTHETICAL CASES